Application API#
Here is listed the completed API available to implement the Application Hooks.
Models#
- data_model(*, caption, icon=None)#
data_modelis an object that keeps together many different properties defined by the plugin and allows developers to build user interfaces in a declarative way.Application Required:
The following options are required when declaring a data_model and are used into the user interface
- Parameters:
caption – A text to be displayed over the Tree.
icon – Name of the icon to be used over the Tree.
Note
Even though the icon parameter is required, it’s not currently being used.
Plugin Defined:
Visual elements that allow the user to input information into the application, or to arrange better the user interface.
- Input Fields:
Visual elements that allow the user to provide input information into the application.
- Layout:
Elements that assist the developer to arrange input fields in a meaningful way.
Check the section visual elements to see all inputs available, and layout elements to see all layouts available.
Example:
@data_model(icon='', caption='My Plugin') class MyModel: distance = Quantity(value=1, unit='m', caption='Distance') @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
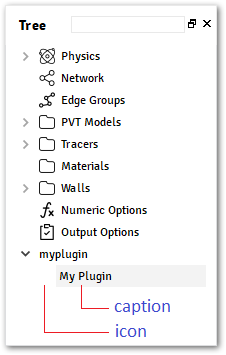
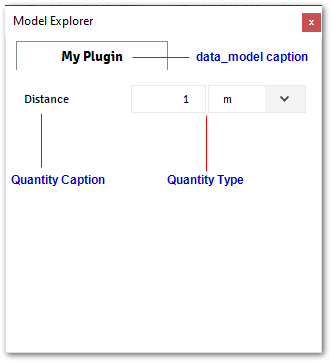
- container_model(*, model, caption, icon=None)#
container_modelis an object that keeps together many different properties defined by the plugin and allows developers to build user interfaces in a declarative way similar todata_model().container_modelcan also hold a reference to adata_model()declared from the plugin, making this object a parent for all newdata_model()created.Application Required:
The following options are required when declaring a
container_model.- Parameters:
caption – A text to be displayed over the Tree.
icon – Name of the icon to be used over the Tree.
model – A reference to a class decorated with
data_model().
Note
Even though the icon parameter is required, it’s not currently being used.
Plugin defined:
Visual elements that allow the user to input information into the application, or to arrange better the user interface.
- Input Fields:
Visual elements that allow the user to provide input information into the application.
- Layout:
Elements that assist the developer to arrange input fields in meaningfully way.
Check the section visual elements to see all inputs available, and layout elements to see all layouts available.
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Child") class ChildModel: distance = Quantity(value=1, unit="m", caption="Distance") @container_model(icon='', caption='My Container', model=ChildModel) class MyModelContainer: my_string = String(value='Initial Value', caption='My String') @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModelContainer]
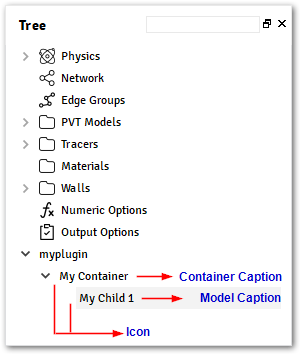
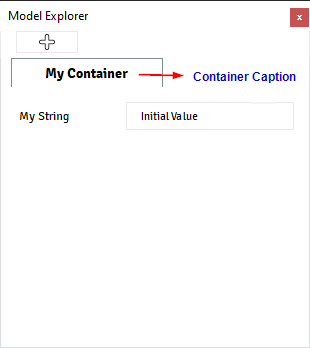
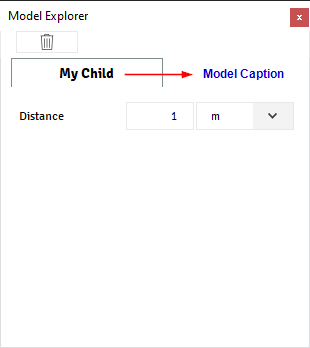
Container data also includes automatically two actions for the model:
Action: Create new Model
An action that creates a new model inside the container selected, you can activate this action by right-clicking in the container over the Tree, or by clicking on the “Plus” icon available at the
Model Explorer.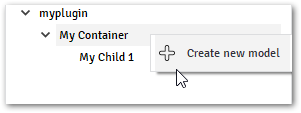
Action: Remove
An action that remove the selected model, only available for models inside a container, you can activate this action by right-clicking the model over the Tree, or by clicking on the “Trash” icon available at the
Model Explorer.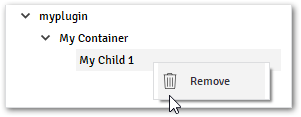

Types#
The types module supplies UI elements for creating user interfaces with the classic desktop-style, each type
has a related model.
Models are the primary elements to create user interfaces on ALFAsim, models can display data, receive user input, and provide a container for other fields that should be grouped together.
- class BaseField#
A base field for all types available at ALFAsim.
- Variables:
caption – Label to be displayed on the right side of the component.
tooltip – Shows a tip, a short piece of text.
enable_expr – Function to evaluate if the component will be enabled or not.
visible_expr – Function to inform if the component will be visible or not.
Caption and Tooltip:
Caption is the most basic information that all fields must inform, it will display Label over the right side of the component on the
Model Explorerwindow.Tooltips are short pieces of text to reminder/inform the user about some specificity about the property when they keep the mouse over the field. Tooltips must be a string and can have HTML tags and Unicode characters as well.
- Raises:
TypeError – if the tooltip informed is not a string.
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon='', caption='My Plugin') class MyModel: my_string_1= String( value='String 1', caption='My String 1', tooltip="Some Text <br> <b> More Information</b>", ) my_string_2 = String( value='String 2', caption='My String 2', tooltip="∩ ∪ ∫ ∬ ∮", ) @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
The images below shows the output from the example above.
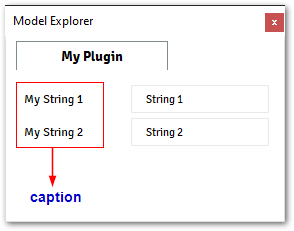
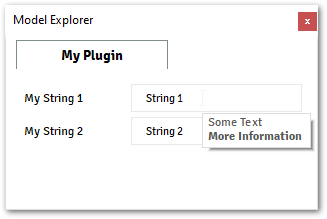
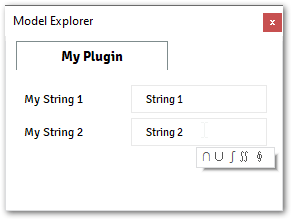
Enable Expression:
Accepts a python function that controls either the component will be enabled, or disabled. The python function will receive two arguments, an instance of itself (to check local values) and an instance of
Contextto retrieve information about the application.This function must return a boolean, informing True (for enabled) or False (for disabled).
enabled: The component will handle keyboard and mouse events.
disabled: The component will not handle events and it will be grayed out.
Example myplugin.py
def my_check(self, ctx): return self.bool_value @data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: bool_value = Boolean(value=True, caption="Enabled") N_ions = Quantity( caption='Number of Ions', value=1, unit='-', enable_expr=my_check, ) @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
The image below shows the
N_ionsproperty disabled, when the propertybool_valueis disabled (False)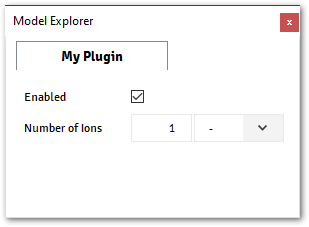
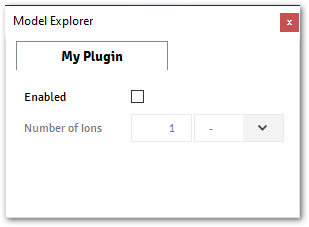
Visible Expression:
Accepts a python function that controls either the component will be visible, or not. The python function will receive two arguments, an instance of itself (to check local values) and an instance of
Context()to retrieve information about the application.This function must return a boolean, informing True (for visible) or False (for invisible).
Example myplugin.py
def my_check(self, ctx): return self.bool_value @data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: bool_value = Boolean(value=True, caption="Enabled") N_ions = Quantity( caption="Number of Ions", value=1, unit="-", visible_expr=my_check, ) @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
The image below shows the
N_ionsproperty visible, when the propertybool_valueis enabled (True)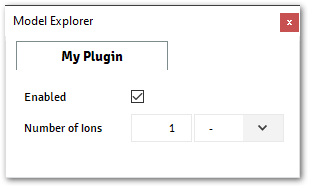
- class String#
The String field represents an input that allows the user to enter and edit a single line of plain text.
The String field have all options available from
BaseField, plus the following ones- Variables:
value – property to hold the value informed by the user.
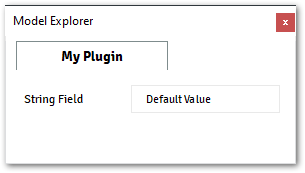
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: string_field = String( value="Default Value", caption="String Field", )
Accessing String Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++ you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_string_size()together withget_plugin_input_data_string_size()Accessing String Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the String field will return the currently text asstr.>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").string_field 'Default Value' >>> type(ctx.get_model("MyModel").string_field) <class 'str'>
- class Enum#
The Enum field provides list of options to the user, showing only the select item but providing a way to display a list of all options through a combo-box.
The Enum field have all options available from
BaseField, besides the listed the ones listed above:- Variables:
values – A list of strings with the available options.
initial – Indicates which one of the options should be selected per default. If not given, the first item in
valueswill be used as default.
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: enum_field = Enum( values=["Option 1, Option 2"], initial="Option 1", caption="Enum Field", )
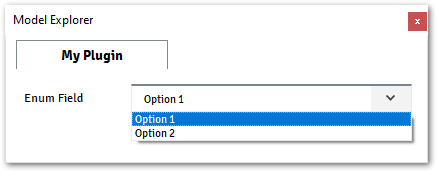
Accessing Enum Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_enum()Accessing Enum Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the Enum field will return the currently selected option asstr.@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: enum_field = Enum( values=["Option 1", "Option 2"], initial="Option 1", caption="Enum Field", )
# From Terminal >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").enum_field 'Option 1' >>> type(ctx.get_model("MyModel").enum_field) <class 'str'>
- class Reference#
The Reference field provides a list of options to the user and displays the current item selected.
There are two types of models supported by this field.
- ALFAsimTypes:
models from ALFAsim, for example, Tracers.
- Custom Data:
a model defined within the plugin.
Note
In order to reference custom data, the model must be inside a container.
- Variables:
caption – Property used as a label for the field.
ref_type – Property that indicates which type of data the Reference will hold.
container_type – The name of the class that holds the ref_type, this property must be used when the
ref_typereferences model from the plugin.
Example using
ALFAsimTypeson myplugin.py@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: tracer_ref = Reference( ref_type=TracerType, caption="Tracer Type", )
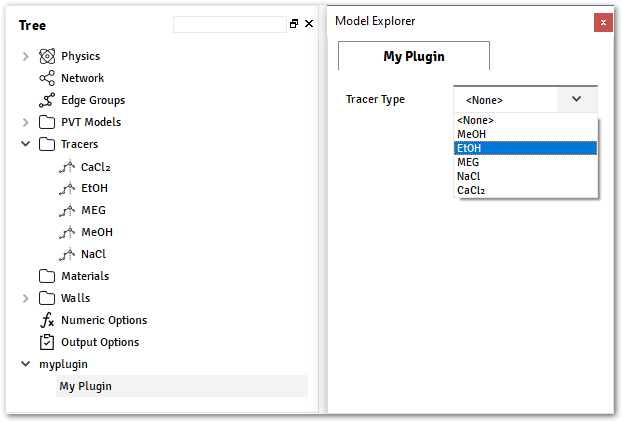
Example using
Custom Dataon myplugin.py@data_model(caption="My Model") class MyModel: field_1 = String(value="Value 1", caption="String 1") @container_model(caption="My Container", model=MyModel, icon="") class MyContainer: internal_ref = Reference( ref_type=MyModel, container_type="MyContainer", caption="Internal Reference", )
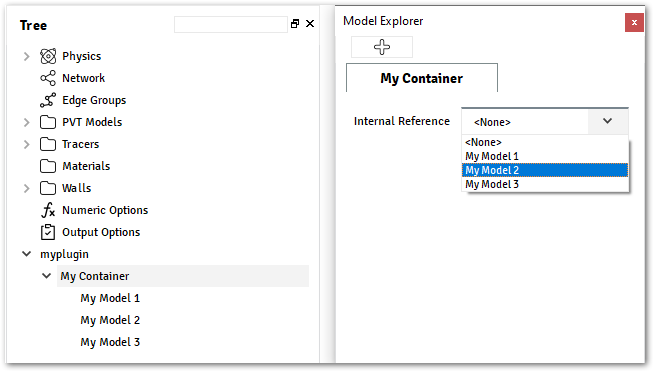
Accessing Reference Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_reference()Accessing Reference Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the Reference field will return the currently selected option object instance.With the instance, you can access all attributes from the object normally. Check the example below.
@data_model(caption="My Model") class MyModel: field_1 = String(value="Value 1", caption="String 1") @container_model(caption="My Container", model=MyModel, icon="") class MyContainer: tracer_ref = Reference( ref_type=TracerType, caption="Tracer Type", ) internal_ref = Reference( ref_type=MyModel, container_type="MyContainer", caption="Internal Reference", ) # Example with Tracer >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").tracer_ref TracerModel(gas_partition_coefficient=[...]) >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").tracer_ref.gas_partition_coefficient Scalar(0.0, 'kg/kg', 'mass fraction') # Example with Custom Data >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").internal_ref MyModel(field_1='Value 1', name='My Model 1') >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").internal_ref.field_1 'Value 1'
- class MultipleReference#
The MultipleReference field works similar to
Reference, providing a list of options to the user, but allowing multiple values, of the same type, to be chosen.There are two types of models supported by this field. :ALFAsimTypes: models from ALFAsim, for example, Tracers. :Custom Data: a model defined within the plugin.
Note
In order to reference a custom data the model must be inside a container.
- Variables:
caption – Property used as a label for the field.
ref_type – Property that indicates which type of data the Reference will hold.
container_type – The name of the class that holds the ref_type, this property must be used when the ref_type references model from the plugin.
Example using
ALFAsimTypeson myplugin.py@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: tracer_ref = MultipleReference( ref_type=TracerType, caption="Tracer Type" )
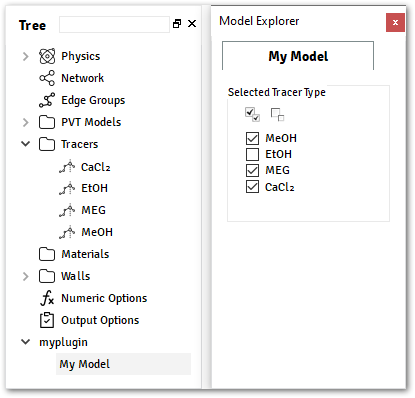
Example using
Custom Dataon myplugin.py@data_model(caption="My Model") class MyModel: field_1 = String(value="Value 1", caption="String 1") @container_model(caption="My Container", model=MyModel, icon="") class MyContainer: internal_ref = MultipleReference( ref_type=MyModel, container_type="MyContainer", caption="Internal Reference", )
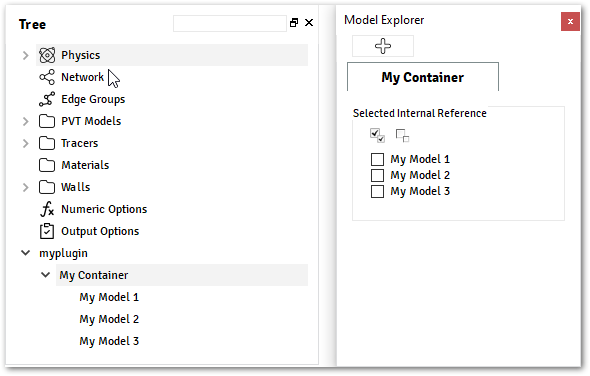
Accessing MultipleReference Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_multiplereference_selected_size()Accessing MultipleReference Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the MultipleReference field will return a list with the currently selected option objects instances.With the instance, you can access all attributes from the object. Check the example below.
@data_model(caption="My Model") class MyModel: field_1 = String(value="Value 1", caption="String 1") @container_model(caption="My Container", model=MyModel, icon="") class MyContainer: internal_ref = MultipleReference( ref_type=MyModel, container_type="MyContainer", caption="Internal Reference", ) # Example >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").internal_ref [MyModel(field_1='Value 1', name='My Model 1'), MyModel(field_1='Value 1', name='My Model 4')] >>> type(ctx.get_model("MyContainer").internal_ref) <class 'list'> >>> ctx.get_model("MyContainer").internal_ref[0] MyModel(field_1='Value 1', name='My Model 1')
- class Quantity#
The Quantity field provides a way to the user provide a scalar value into the application.
The Quantity field have all options available from
BaseField, besides the listed the ones listed above: :ivar values: A number value. :ivar unit: Unit for the given scalar.All scalar values are created using the Barril library
Checkout the Barril documentation, to see all available units
Note
If you want to check the input value, is recommended to include a status monitor in your plugin to make sure that the provided value is valid.
For more details about status monitor check
alfasim_get_status()Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: quantity_field = Quantity( value=1, unit="degC", caption="Quantity Field" )
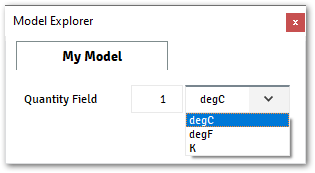
Accessing Quantity Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_quantity()Accessing Quantity Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the Quantity field will return abarril.units.Scalarobject, with the current value and unit. Check out the Scalar documentation from Barril for more details about the usage.@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: quantity_field = Enum( values=["Option 1", "Option 2"], initial="Option 1", caption="Enum Field", ) # From Terminal >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").quantity_field Scalar(1.0, 'degC', 'temperature') >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").quantity_field.value 1.0 >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").quantity_field.unit 'degC' >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").quantity_field.GetValue('K') 274.15
- class Table#
The Table component provides a table to the user to be able input values manually or by importing it from a file.
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Model") class MyModel: Table( rows=[ TableColumn( id="temperature", value=Quantity( value=1, unit="K", caption="Temperature Column Caption", ), ), TableColumn( id="pressure", value=Quantity( value=2, unit="bar", caption="Pressure Column Caption", ), ), ], caption="Table Field", )
The image above illustrates the output from the example above.
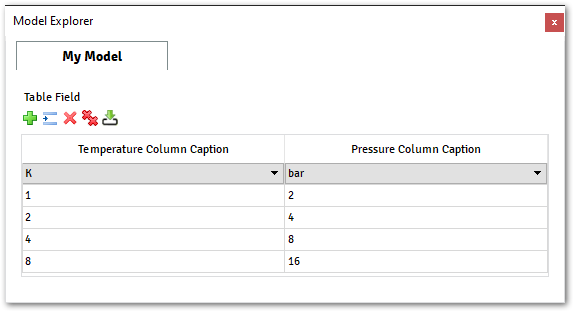
With this component, the user can easily import the content from a file by clicking on the last icon from the toolbar menu.
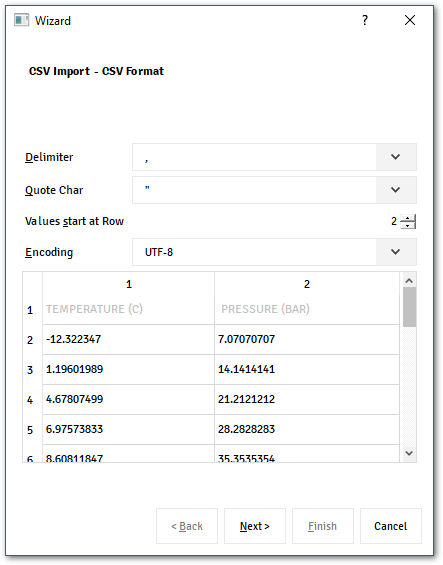
The wizard assistance supports multiple types of file, the user just needs to inform which kind of configuration the file has.
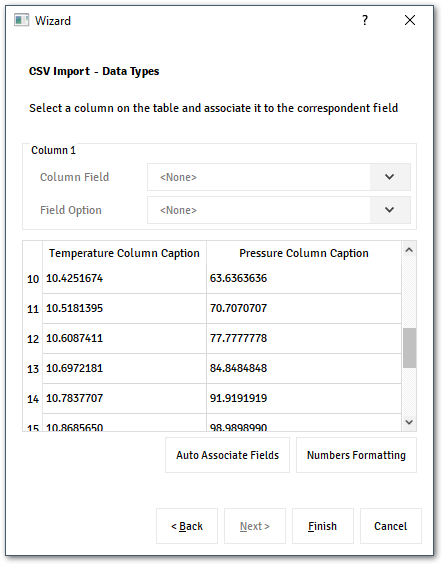
By the end, it’s possible for the user select to which unit the values must be converted and which columns.
Accessing Table Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_table_quantity()Accessing Table Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the Table field will return a model, with information about all columns.1@data_model(icon="", caption="My Model") 2class MyModel: 3 Table( 4 rows=[ 5 TableColumn( 6 id='temperature', 7 value=Quantity(value=1, unit='K', caption='Temperature Column Caption'), 8 ), 9 TableColumn( 10 id='pressure', 11 value=Quantity(value=2, unit='bar', caption='Pressure Column Caption'), 12 ), 13 ], 14 caption="Table Field" 15 ) 16 17# From Terminal 18>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").table_field 19TableContainer([...]) 20 21>>> len(ctx.get_model("MyModel").table_field) 226 23 24>>> len(ctx.get_model("MyModel").table_field) 25TableRow(temperature=Scalar(1.0, 'K', 'temperature'), pressure=Scalar(2.0, 'bar', 'pressure')) 26 27>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").table_field[0].pressure 28Scalar(2.0, 'bar', 'pressure')
- class TableColumn#
The TableColumn component provides columns for a
Tablefield. Currently only columns with aQuantityfields are available.Check out the documentation from
Tableto see more details about the usage and how to retrieve values.
- class Boolean#
The Boolean field provides a checkbox to select/deselect a property.
The Boolean fields have all options available from
BaseField, besides the listed the ones listed above: :ivar value: A boolean informing the initial state from the FieldExample myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: boolean_field = Boolean( value=False, caption="Boolean Field", )
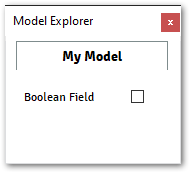
Accessing Boolean Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_boolean()Accessing Quantity Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the Boolean field will return a boolean value@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: quantity_field = Boolean( value=False, caption="Boolean Field", ) # From Terminal >>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").boolean_field False
- class FileContent#
The FileContent component provides a platform-native file dialog to the user to be able to select a file. The name of the selected file will be available over the GUI.
Note
If you want to make the file mandatory it is recommended to include a status monitor in your plugin to make sure that a file is selected.
For more details about status monitor check
alfasim_get_status()- Variables:
caption – Label to be displayed on the right side of the component.
Example myplugin.py
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Plugin") class MyModel: file_content_field = FileContent(caption="FileContent Field")
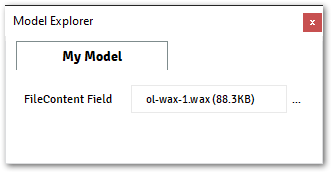
Accessing FileContent Field from Plugin:
In order to access this field from inside the plugin implementation, in C/C++, you need to use
get_plugin_input_data_file_content()together withget_plugin_input_data_file_content_size()Accessing Quantity Field from Context:
When accessed from the
Context, the FileContent field will return a FileContent object, a Model that represent a file from the filesystem.Class FileContent
- Variables:
path – Return a Path object of the file.
content – The content from the file in binary format.
size – The size of the file in bytes.
modified_date – Return a Datetime object, with the last time the file was modified
>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").file_content_field.path WindowsPath('C:/ol-wax-1.wax')
>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").file_content_field.content b"!Name of Table [...] "
>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").file_content_field.size 90379
>>> ctx.get_model("MyModel").file_content_field.modified_date datetime.datetime(2019, 5, 10, 14, 22, 11, 50795)
Layout#
- group()#
The group layout is a container to organize ALFAsim types, only fields that derives from BaseField can be defined inside a group.
Example.:
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Model") class MyModel: string_field_1 = String(caption="Outside", value="Default") @group(caption="Group Container") class GroupMain: string_field_2 = String(value="Group 1", caption="Inside") bool_field = Boolean(value=True, caption="Boolean Field")
The image below shows the output from the example above.
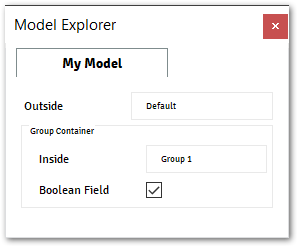
Note
groupis a layout component, and will not have an attribute to be accessed through context or API.
- tabs()#
Create a tab bar layout, to group multiples :func:”tab” instances.
With the
tabs, you can split up complex dialog into “pages” using a :func:”tab” instance.Notice that only classes decorated with :func:”tab” can be placed inside a
tab bar.Example of usage:
@data_model(icon="", caption="My Model") class MyModel: field = String(caption="String outside tabs", value="Default") @tabs() class MainPage: @tab(caption="Fist Tab") class Tab1: field_1 = String(caption="First Tab", value="Default") @tab(caption="Second Tab") class Tab2: field_2 = String(caption="Second Tab", value="Default")
The image below shows the output from the command above.
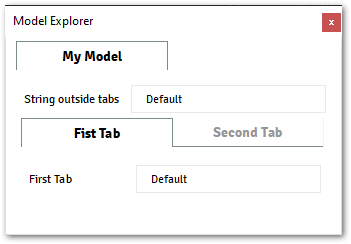
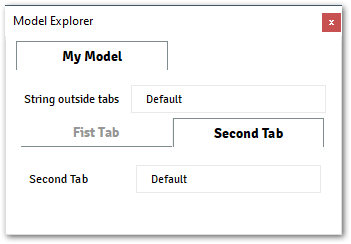
Note
tabsis a layout component, and will not have an attribute to be accessed through context or API.
- tab()#
The tab represents a single entry, on the
tabs()layout.Notice that only components available at the types modules can be placed inside a tab.
Status#
- class ErrorMessage#
ErrorMessage allows the plugin to display a message over the status monitor, and signalize to the application to block the simulation until the issue is fixed.
- Variables:
model_name – Name of the model that issues the error.
message – Message that will be displayed over the status monitor.
Checkout the
alfasim_get_status()for some examples of`ErrorMessage`in action.
- class WarningMessage#
WarningMessage allows the plugin to display a message to the user over the status monitor, and signalizes a minor issue that needs to be fixed but doesn’t block the simulation.
- Variables:
model_name – Name of the model that issues the warning.
message – Message that will be displayed over the status monitor.
Checkout the
alfasim_get_status()for some examples of`WarningMessage`in action.
Context#
- class Context#
The context class provides information about the current state of the application and the models implemented by the user.
The following methods provide an instance of
Contextto inform the current state of the application:Visible Expression: parameter from all fields
Enable Expression: parameter from all fields
alfasim_get_status()hook
- get_edges()#
Return a list of all Edges available on ALFAsim. Each Edge is represented by an instance of
EdgeInfo.Example of GetEdges
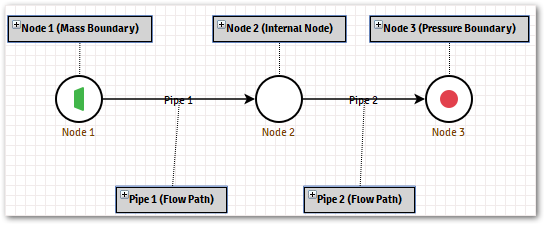
The image above has two Edges configured, in order to access the available Edges, it’s possible to use the method
get_edgesas demonstrated below.Accessing GetEdges from the context
>>> ctx.get_edges()[0] EdgeInfo(name='Pipe 1', number_of_phases_from_associated_pvt=2) >>> ctx.get_pipelines()[0].number_of_phases_from_associated_pvt 'Pipe 1'
Checkout the
EdgeInfosection to know more about the properties available.
- get_model(model_name)#
Returns an instance of the given
model_name.- Parameters:
model_name – must be the name of a model defined within the plugin.
In the example below, the
Contextis used to access a property from the modelMyModelctx.GetModel("Acme")as exemplified in the code below.Setting up the model
@data_model(caption="MyPlugin", icon="") class MyModel: name = String(value="ALFAsim", caption="Field") scalar = Quantity(value=1, unit="degC", caption="Field") @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
Accessing the context
>>> ctx.get_model('MyModel') MyModel(name='ALFAsim', scalar=Scalar(1.0, 'degC', 'temperature')) >>> ctx.get_model('MyModel').name 'ALFAsim'
At runtime, you can also verify the names of the models defined by a given plugin. For more information check cpp:func:~alfasim_sdk.context.Context.GetPluginInfoById
- Raises:
TypeError – When the given
model_namedoes not exist.FrozenInstanceError – When trying to modify a value
- get_nodes()#
Return a list of all Nodes available on ALFAsim. Each Node is represented by an instance of
NodeInfo.Usage Example of GetNodes

The image above has three nodes configured, you can access this information by using the method
get_nodesas demonstrated below.>>> ctx.get_nodes[0] NodeInfo(name='Node 1', number_of_phases_from_associated_pvt=2) >>> ctx.get_nodes[0].name 'Node 1'
Note
The values from NodeInfo are read-only, they cannot be modified.
Checkout the
NodeInfosection to know more about the properties available.
- get_physics_options()#
Return the physics options from the current project from ALFAsim.
Example of GetPhysicsOptions
The image below shows a configuration from a given project.
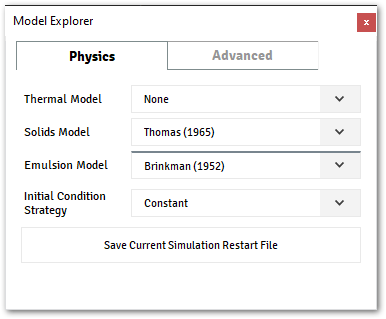
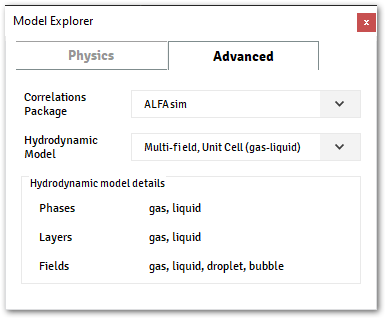
It’s possible to access this information from inside the plugin, by using context api as demonstrate below.
Accessing GetPhysicsOptions from the context
>>> ctx.get_physics_options() PhysicsOptionsInfo( [...] ) >>> ctx.get_physics_options().emulsion_model.value EmulsionModelInfo( [ ... ] ) >>> ctx.get_physics_options().hydrodynamic_model HydrodynamicModelInfo( [ ... ] ) >>> ctx.get_physics_options().hydrodynamic_model.fields ['gas', 'oil', 'droplet', 'bubble'] >>> ctx.get_physics_options().hydrodynamic_model.layers ['gas', 'oil'] >>> ctx.get_physics_options().hydrodynamic_model.phases ['gas', 'oil']
Checkout the
PhysicsOptionsInfosection to know more about the properties available.
- get_pipelines()#
Return a list with all Pipes available on the Network from the Project. Each Pipe is represented by an instance of
PipelineInfo.Usage Example of GetPipelines

The image above has two Pipelines configured, you can access this information by using the method
GetPipelinesas demonstrated below.>>> ctx.get_pipelines()[0] PipelineInfo(name='Pipe 1 > Pipeline', [ ... ]) >>> ctx.get_pipelines()[0].edge_name 'Pipe 1' >>> ctx.get_pipelines()[0].total_length Scalar(1000.0, 'm', 'length') >>> len(ctx.get_pipelines()[0].segments) 1
Note
The values from PipelineInfo are read-only, they cannot be modified.
Checkout the
PipelineInfosection to know more about the properties available.
- get_plugin_info_by_id(plugin_id)#
Similar to
get_plugins_infos()but returns a single instance ofPluginInfofrom the givenplugin_idparameter.Checkout the
PluginInfosection to know more about the properties available.- Raises:
ValueError – When the plugin informed by
plugin_idit’s not available.
- get_plugins_infos()#
Return a list of all plugins available on ALFAsim. Each plugin is represented by an instance of
PluginInfo.Usage Example of GetPluginsInfos
The example demonstrated how you can access information about the plugin from using the cpp:func:~alfasim_sdk.context.Context.GetPluginsInfos method.
Setting up the model
@data_model(caption="MyPlugin", icon="") class MyModel: name = String(value="ALFAsim", caption="Field") scalar = Quantity(value=1, unit="degC", caption="Field") @alfasim_sdk.hookimpl def alfasim_get_data_model_type(): return [MyModel]
Accessing the context
>>> ctx.get_plugins_infos() [PluginInfo(caption='myplugin', name='myplugin', enabled=True, models=['MyModel'])] >>> ctx.get_plugins_infos()[0].enabled True >>> ctx.get_plugins_infos()[0].models ['MyModel']
Checkout the
PluginInfosection to know more about the properties available.
- class EdgeInfo(name, number_of_phases_from_associated_pvt)#
The
EdgeInfoprovides information about aEdgefromALFAsim, it provides the name of the Node and the number of phases that the associate pvt model has.
- class EmulsionModelInfo(enabled, relative_viscosity_model, droplet_size_model, inversion_point_model)#
EmulsionModelInfo provides information about whether the emulsion model is enabled and the models used for relative viscosity, droplet size, and inversion point.
- class HydrodynamicModelInfo(selected_base_type, phases, fields, layers, has_water_phase)#
HydrodynamicModelInfo provides information about which layer, fields, and phases the currently Hydrodynamic model is using.
- class NodeInfo(name, number_of_phases_from_associated_pvt)#
The
NodeInfoprovides information about aNodefromALFAsim, it provides the name of the Node and the number of phases that the associate PVT model has.
- class PhysicsOptionsInfo(emulsion_model, solids_model, hydrodynamic_model)#
PhysicsOptionsInfoprovides information about the physics options available atALFAsim.The following option can be accessed:
Emulsion Model: Informs the relative viscosity, droplet size, and inversion point emulsion models
Solids Model: Informs the current solid model being used by the application For more information about all options available check
SolidsModelTypeHydrodynamic Model: Provides a
HydrodynamicModelInfoinforming which layers, fields and phases the application is currently using.
- class PipelineInfo(name, edge_name, segments, total_length)#
The PipelineInfo provides information about the geometry of a pipeline.
PipelineSegmentInfo provides the following attributes: :ivar name: Name associated with this
Pipelineon ALFAsim- Variables:
edge_name – Name of the edge that this
Pipelineis associated with.segments – List of segments associates with this
PipelineFor more information checkPipelineSegmentInfototal_length – Total length of the pipeline.
- class PipelineSegmentInfo(inner_diameter, start_position, is_custom, roughness)#
The PipelineSegmentInfo provides information about segments associated with a pipeline.
PipelineSegmentInfo provides the following attributes:
- Variables:
start_position – Defines point where this segment starts in MD (measured depth).
inner_diameter – Inner diameter of pipe annulus.
roughness – Absolute roughness of the wall of this segment. When
`is_custom`is true, the reported roughness is customized for this segment, otherwise, the reported roughness is the original reported by the wall.is_custom – Informs either the roughness value is custom or original from the wall
- class PluginInfo(caption, name, enabled, models)#
PluginInfo provides information about the plugin name, its current state (either enabled or not) and all models defined from this plugin.